Deployment Platform/Software
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Harmonic Distribution version cycle: | 1.0 | Factory |
Software Map
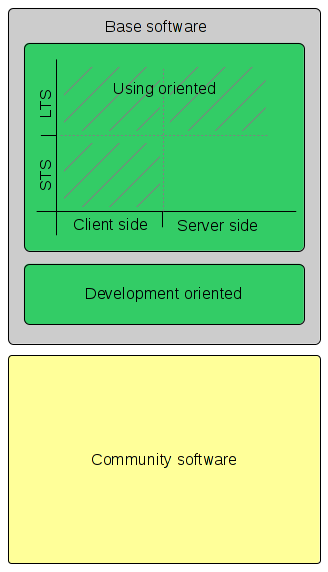
|
The whole software within the Harmonic Distribution is structured as:
|
Shell
Stable Glucose releases.
Doers' Kit
Sugar Doers Kit (SDK) is a set of tools and libraries to help people code in Sugar.
- Sweets, Zero Install based Package Management System for Sugar.
- sugar-lint, utility to lint various source files.
- gatch, support long or ever standing, all time being on top, downstream patchset for the base branch in a Git repository.
- Sugar via Sweets, several Sucrose versions via Sweets.
Glucose development
Server Kit
For detailed information, see Server Kit's home page.
Sugar Network
- active-document library.
- restful-document library.
- sugar-network client library.
- sugar-network-server server.
Distribution via Sugar Network
The high-level overview is looks like:
- software creators
upload source bundles to the Sugar Network; only sources, even if it is binary based activities; - Sugar Network
if uploaded software needs building, it will send it to OBS; - on users side
Sweets library will:- read Sugar Network to find out information about implementations of software that user requested to launch;
- according to the local environment, it will download proper implementation;
- if there is no proper binary implementation, it will download sources and will build them in local environment.