Homepage | Activities | Events | Lists | Development | Translate | Contact
Activities/Measure
About
This Activity draws a picture of the sound heard by the internal microphone or of the signal present on the microphone socket. More specifically it draws a graph of this input versus time, the input is on the vertical axis and time is on the horizontal axis. That is, the laptop functions like a machine called an oscilloscope.
As well as graphing signal as a function of time, Measure can also graph as a function of frequency.
The XO-1 laptop is only capable of mono input, the XO-1.5 and XO-1.75 are capable of stereo input on their microphone socket and can graph two signals at once.
Using
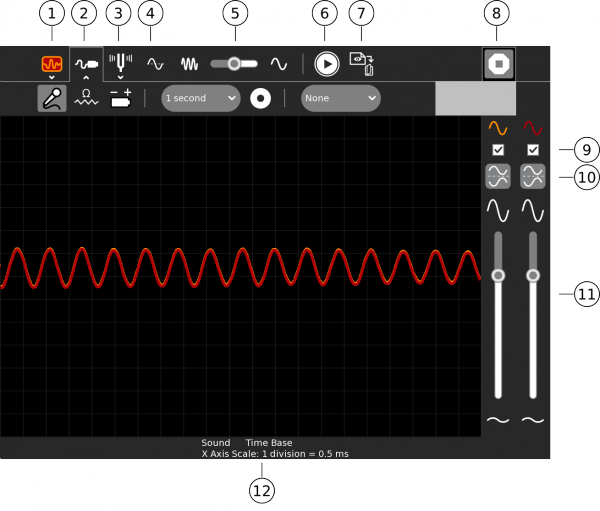
1. Select secondary toolbar - allows the Activity's Journal entry to be renamed
2. Select secondary toolbar - measurement settings
3. Select secondary toolbar - tuning settings
4. The selected input type - Sound (AC voltage), resistance or DC voltage
5. The time scale
6. Freeze the display
7. Capture sample now - saves an image of the wave in the Journal
8. Stop - exits the Activity
9. Mute - mute/unmute channel
10. Invert - invert the display
11. Use these sliders to control the sensitivity
12. The settings that are selected
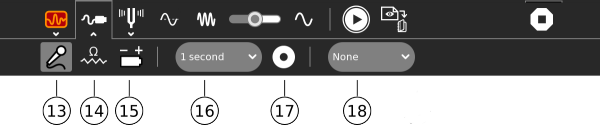
The sensor toolbar - measurement settings
13. Sound - use this setting with the internal microphone, external microphone and external AC signals
14. Resistance sensor - use with external resistive type transducers
15. Voltage sensor - use with external sensors which generate a voltage
16. Time base/frequency - graphs the signal vs. time or graphs amplitude vs. frequency
17. Sample interval - a text file 'Measure Log' is saved to the journal, it contains one sample per interval
18. Starts/stops saving a text file 'Measure Log' with measured values as readable text
19. Trigger - synchronise the sample period to the waveform so that the sample will start on a rising edge or falling edge
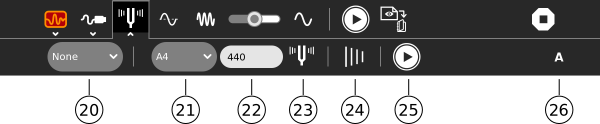
The tuning toolbar - frequency settings
Hint: Adjust the time scale (#5) to increase the spacing between the tuning lines.
20. Instrument - select instrument to tune
21. Frequency entry - enter a frequency to mark
22. Show frequency.
Applying
Let the children experiment with the internal microphone, try singing, whistling, musical instruments, the Tam Tam musical Activity. The Turtle Blocks Activity can generate an audio tone, see the Python Block.
The children should learn through guided discovery that:
- sound is a pressure wave
- the pitch of the sound is determined by the frequency or cycles per second (Hz)
- the loudness of a sound is determined by the amplitude
- sounds contain multiple frequency components or harmonics
- the more pure sounds have less harmonics
Sharing
This Activity does not support sharing.
Extending
Measure is able to take input from a wide range of external sensors including switches, photocells, temperature sensors, inductive loops, hall effect sensors, soil probes and many more.
Care should be taken not to exceed the allowable input voltage:
- XO-1 -0.5V to 5V
- XO-1.5 -6V to +9V
- XO-1.75 -6V to +9V
It is a good idea, particularly on the XO-1, to put a resistor of 680 ohms in the phono plug, this increases the allowable input voltage range.
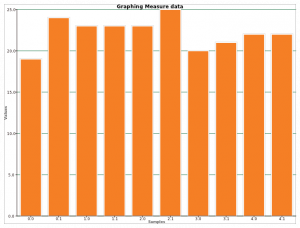
Plotting
You can use save data from measure to the Sugar Journal using the Capture feature described above (16). These data can then be imported into SimpleGraph, where they are displayed.
More ideas
You can find ideas for fun science experiments at http://wiki.sugarlabs.org/go/Activities/TurtleArt/Using_Turtle_Art_Sensors and http://wiki.laptop.org/go/Measure
Building sensors
There are detailed instructions for building sensors at [1].