Activities/Abacus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:Abacus.jpg]] | [[File:Abacus.jpg]] | ||
[[File:Abacus-activity.png]] | |||
== Where to get Abacus == | == Where to get Abacus == | ||
| Line 123: | Line 125: | ||
File:Abacus-fractions.png|20 + 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/6 = 22 | File:Abacus-fractions.png|20 + 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/6 = 22 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=== The toolbars === | === The toolbars === | ||
| Line 249: | Line 206: | ||
* Abacus also supports copy, so you can take a sum calculated on an abacus and export it into SimpleGraph or some other data-visualization Activities. | * Abacus also supports copy, so you can take a sum calculated on an abacus and export it into SimpleGraph or some other data-visualization Activities. | ||
== Modifying Abacus == | |||
Abacus is under GPL license. You are free to use it and learn with it. You are also encouraged to modify it to suit your needs or just for a further opportunity to learn. | |||
Most changes can be confined to three modules: <code>AbacusActivity.py</code>, <code>abacus.py</code> and <code>abacus_window.py</code>. The former define the Sugar and GNOME toolbars; the latter defines what code is executed by each type of abacus. | |||
'''Note: since a recent refactoring, these instructions are deprecated''' | |||
For instance, to add a menu item such as 'Reset' you would do the following in <code>abacus.py</code>: | |||
* Add these lines to the menu items list: | |||
menu_items = gtk.MenuItem(_("Reset")) | |||
menu.append(menu_items) | |||
menu_items.connect("activate", self._reset) | |||
* The _reset() method is trivial: | |||
def _reset(self, event, data=None): | |||
""" Reset """ | |||
self.abacus.mode.reset_abacus() | |||
Similarly, you can add another button to the Sugar toolbar in <code>AbacusActivity.py</code>: | |||
* Add these lines to the toolbar block: | |||
# Reset the beads on the abacus to the initial cleared position | |||
self.reset_button = ToolButton( "reset" ) | |||
self.reset_button.set_tooltip(_('Reset')) | |||
self.reset_button.props.sensitive = True | |||
self.reset_button.connect('clicked', self._reset_button_cb) | |||
toolbar_box.toolbar.insert(self.reset_button, -1) | |||
self.reset_button.show() | |||
* The _reset_button_cb() method is trivial: | |||
def _reset_button_cb(self, event, data=None): | |||
""" Reset the beads on the abacus to the initial cleared position """ | |||
self.abacus.mode.reset_abacus() | |||
* You'll have to create an icon for the button (<code>reset.svg</code>) and put it into the <code>icon</code> subdirectory of the bundle. | |||
This will complete the changes in the <code>abacus.py</code>. The method <code>reset_abacus()</code> will have to be defined for each abacus in the <code>abacus_window.py</code>. This can be done by creating that method in the <code>AbacusGeneric</code> class used by all the varieties of abacus. The method may have to be overridden in some abacus subclasses for customization reasons. For instance, <code>reset_abacus()</code> was defined in <code>AbacusGeneric</code> class and then overridden in <code>Schety</code>. | |||
If the changes involve modifying the graphics, then other methods may need to be modified as well. For instance, in order to introduce a reset button that can be clicked to reset the bead positions to the beginning, the following methods had to be modified – all in <code>abacus_window.py</code>: | |||
# in the <code>class Abacus</code>, method <code>_button_press_cb()</code> to activate reset button; | |||
# in the <code>class AbacusGeneric</code>, method <code>create()</code> to create the graphics for reset button; | |||
# methods <code>hide()</code> and <code>show()</code> to make the button visible. | |||
== Reporting problems == | == Reporting problems == | ||
Revision as of 11:06, 7 April 2012
About Abacus
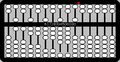
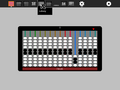
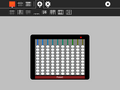
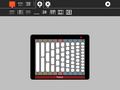
Abacus lets the learner explore different representations of numbers using different mechanical counting systems developed by the ancient Romans and Chinese. There are several different variants available for exploration: a suanpan, the traditional Chinese abacus with 2 beads on top and 5 beads below; a soroban, the traditional Japanese abacus with 1 bead on top and 4 beads below; the schety, the traditional Russian abacus, with 10 beads per column, with the exception of one column with just 4 beads used for counting in fourths; and the nepohualtzintzin, a Mayan abacus, 3 beads on top and 4 beads below (base 20). There is also a binary abacus, a hexadecimal abacus, and several abacuses that lets you calculate with common fractions: 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/6, 1/8, 1/9, 1/10, and 1/12. As of Version 9, there is a customization toolbar that lets you design your own abacus. There is an Incan abacus (Yupana) as a standalone program.
Where to get Abacus
Using Abacus
Clearing the abacus
Before you start an arithmetic operation, you need to "clear" the abacus. The upper beads should be positioned against the top of the frame and the lower beads should be positioned against the bottom of the frame. This is the default position for the abacus when you launch the activity. (Note that some of the abacuses (e.g., the schety) do not have any upper beads. In such cases, all of the beads should start in the down position.)
Reading the abacus
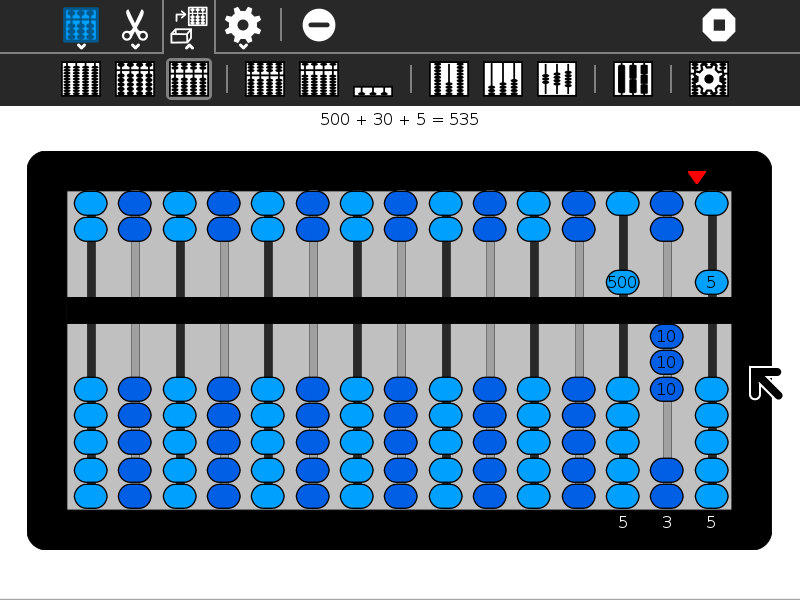
In each column, the bottom beads represent 1s and the top beads represent 5s. (The exception is the column in the schety with only 4 beads. These are 1/4 each.) So for each bead you raise up from the bottom in a column add 1 and for each bead you lower from the top in the same column, add 5.
The columns themselves represent decimal positions from right to left, e.g., 1s, 10s, 100s, 1000s, etc. (There are some exceptions: (1) the nepohualtzintzin uses base 20, e.g., 1s, 20s, 400s, 8000s, etc.; (2) on the schety, the beads to the right of the column with just four beads are 0.1s, 0.01s, 0.001s, and 0.0001s; the black beads on the Caacupé abacus are fractions; and the custom abacus lets you choose whatever (integer) base you want.)
The current value is always displayed on the frame. Experiment and you will quickly learn to write and read numbers.
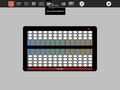
Examples: In the gallery below, several simple examples are shown. In the gallery of images above, the number 54321 is shown on each of the different abaci.
-
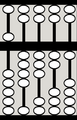
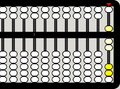
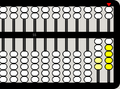
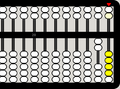
1 bottom bead is up, corresponding to 1 unit
-
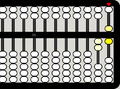
1 top bead is down, corresponding to 5 units
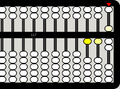
-
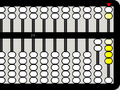
5 bottom beads are up, also corresponding to 5 units
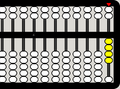
-
1 bottom bead is up and 1 top bead is down, corresponding to 6 units
-
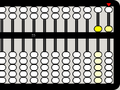
5 bottom beads are up and 1 top bead is down, corresponding to 10 units (time to "carry" to the left)
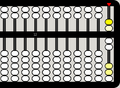
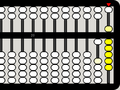
-
This 10 is equivalent to...
-
... this 10
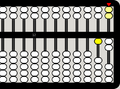
-
54321
Note: The display always assumes a fixed unit column, but you can override this choice.
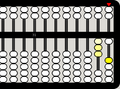
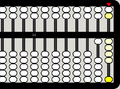
-
The beads moved most recently are highlighted.
Addition
To add, simply move in more beads to represent the number you are adding. There are two rules to follow: (1) whenever you have a total of 5 units or more on the bottom of a column, cancel out the 5 by sliding the beads back down and add a five to to the top; and (2) whenever you have a total of 10 units or more in a column, cancel out the 10 and add one unit to the column immediately to the left. (With the nepohualtzintzin, you work with 20 rather than 10.)
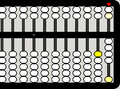
Example: 4+3+5+19+24=55
-
4
-
+3=7 (5–2=3)
-
+5=12
-
carry 5s to next column
-
+19=31 (20-1=19)
-
+24=55
-
4+3+5+19+24=55
Subtraction
Subtraction is the inverse of addition. Move out beads that correspond to the number you are subtracting. You can "borrow" from the column immediately to the left: subtracting one unit and adding 10 to the current column.
Example: 26–2–4–6–10=4
-
26
-
26–2=24
-
24–4=20
-
carry 10 to the right
-
20–6=14
-
14–10=4
Multiplication
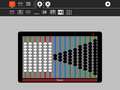
There are several strategies for doing multiplication on an abacus. In the method used in the example below, the multiplier is stored on the far left of the abacus and the multiplicand is offset to the left by the number of digits in the multiplier. The red indicator is used to help keep track of where we are in the process.
-
486×24=? Begin by placing 24 in the left-most columns and 486 offset from the far right by two columns (since 24 has two digits). Set the indicator to the right of the multiplicand.
-
Multiply the least-significant digits (LSD) of the multiplier (4) and multiplicand (6) and place the results (4×6=24) in the far right columns.
-
Multiply the next digit in the multiplier (2, which corresponds to 2×10=20) and the LSD of the multiplicand (6) and add the results (2×6=12) on the right (advancing one column to the left to correspond to the power of the digit in the multiplier).
-
Move the indicator over one column to the left.
-
Repeat for the next digit in the multiplicand (8): 4×8=32
-
2×8=16
-
Move the indicator over one column to the left.
-
Repeat for the next digit in the multiplicand (4): 4×4=16
-
2×4=8
-
Clear the multiplier from the left and view the result: 486×24=11664
Division
Simple division (by a single-digit number) is the inverse of multiplication. In the example below, the dividend is put on the left (leaving one column vacant for the quotient) and the divisor on the right.
-
123456789÷2=? Place the dividend (123456789) on the left, leaving one blank column. Place the divisor (2) on the right.
-
Working from the left to the right, divide a digit in the quotient and then move the indicator one column to the right. 1÷2=0.5
-
2÷2=1
-
3÷2=1.5
-
4÷2=2
-
5÷2=2.5
-
6÷2=3
-
7÷2=3.5
-
8÷2=4
-
9÷2=4.5
-
The result is 61728394.5.
TODO: Add instructions for long division.
Fractions
The fraction abacus lets you add and subtract common fractions: 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/6, 1/8, 1/9, 1/10, and 1/12, The fractional value is determined by the number of black beads on a rod, e.g., to work with thirds, use the rod with three beads, to work with fifths, use the rod with five beads.
The rods with white beads are whole numbers in base 10; from left to right 100000, 10000, 1000, 100, 10, and 1.
-
20 + 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/6 = 22
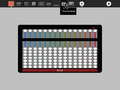
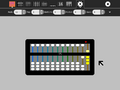
The toolbars
-
suanpan (Chinese)
-
soropan (Japanese)
-
schety (Russian)
-
nepohualtzintzin (Mayan)
-
binary (base 2)
-
hexadecimal (base 16)
-
fractions (1/2, 1/3, 1/4,...)
-
Caacupe (fractions with +/–)
-
decimal (base 10)
-
Cuisenaire-style rods (fractions)
-
custom, as shown: octal (base 8)
Learning with Abacus
It would be interesting to discuss various lesson plans for using an abacus here. Also, it would be interesting to explore the use of color. What if, for example, the more recent a bead is moved, the more colorful it is? (implemented in v5). This would perhaps make it more clear what the order of operations is on a calculation. Also, what it we extend the idea of the schety to include more fractional components, e.g., 3rd, 5ths, 6ths, etc. and perhaps have a mode where we can automate the consolidation of the fractional parts (implemented in v6).
Might be good to have some of the above information in Help, eg addition, subtraction, multiplication division. Just the text, no graphics?
It was proposed in IRC last night that a fun collaborative mode might be to have a number randomly generated and each sharer work independently to post it on the abacus of their choice first. There could be a tally of beads awarded for each correct answer. Maybe something to add to v10.
I wonder, should the beads on the fraction abacus vary in size? The halves should be five-bead heights each, for example?
As of v10, the beads are labeled.
Extending Abacus
- A fun project is to compare calculations using Abacus with the Calculate Activity. Which is faster? Which is more accurate? Which is better for estimating? Which is better for comparing?
- Abacus supports paste, so you can take numeric values from other programs and paste them into the abacus to see what their representations are; for example, I often paste numbers into the hexadecimal abacus as a quick way of converting decimal to hexidecimal.
- Abacus also supports copy, so you can take a sum calculated on an abacus and export it into SimpleGraph or some other data-visualization Activities.
Modifying Abacus
Abacus is under GPL license. You are free to use it and learn with it. You are also encouraged to modify it to suit your needs or just for a further opportunity to learn.
Most changes can be confined to three modules: AbacusActivity.py, abacus.py and abacus_window.py. The former define the Sugar and GNOME toolbars; the latter defines what code is executed by each type of abacus.
Note: since a recent refactoring, these instructions are deprecated
For instance, to add a menu item such as 'Reset' you would do the following in abacus.py:
- Add these lines to the menu items list:
menu_items = gtk.MenuItem(_("Reset"))
menu.append(menu_items)
menu_items.connect("activate", self._reset)
- The _reset() method is trivial:
def _reset(self, event, data=None):
""" Reset """
self.abacus.mode.reset_abacus()
Similarly, you can add another button to the Sugar toolbar in AbacusActivity.py:
- Add these lines to the toolbar block:
# Reset the beads on the abacus to the initial cleared position
self.reset_button = ToolButton( "reset" )
self.reset_button.set_tooltip(_('Reset'))
self.reset_button.props.sensitive = True
self.reset_button.connect('clicked', self._reset_button_cb)
toolbar_box.toolbar.insert(self.reset_button, -1)
self.reset_button.show()
- The _reset_button_cb() method is trivial:
def _reset_button_cb(self, event, data=None):
""" Reset the beads on the abacus to the initial cleared position """
self.abacus.mode.reset_abacus()
- You'll have to create an icon for the button (
reset.svg) and put it into theiconsubdirectory of the bundle.
This will complete the changes in the abacus.py. The method reset_abacus() will have to be defined for each abacus in the abacus_window.py. This can be done by creating that method in the AbacusGeneric class used by all the varieties of abacus. The method may have to be overridden in some abacus subclasses for customization reasons. For instance, reset_abacus() was defined in AbacusGeneric class and then overridden in Schety.
If the changes involve modifying the graphics, then other methods may need to be modified as well. For instance, in order to introduce a reset button that can be clicked to reset the bead positions to the beginning, the following methods had to be modified – all in abacus_window.py:
- in the
class Abacus, method_button_press_cb()to activate reset button; - in the
class AbacusGeneric, methodcreate()to create the graphics for reset button; - methods
hide()andshow()to make the button visible.
Reporting problems
If you discover a bug in the program or have a suggestion for an enhancement, please file a ticket in our bug-tracking system.
You can view the open tickets here.