Difference between revisions of "Documentation Team/User Manual"
m (update link to glossary) |
m (Update links) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li> Connect to the Internet. (For details, see [[Connecting to the Internet]]) | + | <li> Connect to the Internet. (For details, see [[DocumentationTeam/User Manual/Connecting to the Internet]]) |
<li> Open a Linux prompt. (For details, see [[#How do I access a Linux command prompt?|How do I access a Linux command prompt?]] Note that unless you are an advanced user, you should use the Terminal Activity button to open the prompt.) | <li> Open a Linux prompt. (For details, see [[#How do I access a Linux command prompt?|How do I access a Linux command prompt?]] Note that unless you are an advanced user, you should use the Terminal Activity button to open the prompt.) | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
*“simple” mesh network, which lets you collaborate directly with other XOs. | *“simple” mesh network, which lets you collaborate directly with other XOs. | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | Read [[Connecting to the Internet]] for detailed instructions. | + | Read [[DocumentationTeam/User Manual/Connecting to the Internet]] for detailed instructions. |
===Connecting to Jabber Servers=== | ===Connecting to Jabber Servers=== | ||
Revision as of 09:32, 1 November 2008
How To Use Sugar
Using the Interface
Where's the desktop?
Sugar is a different desktop environment to what is normally used in Windows, Apple's OS X or other Linux operating systems. The first thing that a child sees, therefore, is not a hard disk or a trash can — it’s the other children in the “neighborhood.” Sugar's closest desktop metaphor is the Home view: where the user can see what Activities they are currently using and access the Journal, which acts as a history of usage and allows the user to access files they viewed or applications they ran previously.
Using Activities
What is an Activity?
The program that you run using Sugar are called Activities. Why? Because Sugar, in its departure from the desktop metaphor for computing, is the first serious attempt to create a user interface that is based on both cognitive and social constructivism: an environment where learners engage in authentic exploration and collaboration in the act of learning.
Starting an Activity
Installing and Deleting Activities
- Installing Sugar Activities Using Browse
- Installing/Removing Sugar Activities Using Terminal
- Installing/Removing Linux Applications
- Installing Sugar Coated Linux Applications
- Windows Applications
Customizing the Interface
Changing an XO's Nickname and Color on Sugar Views
- Your XO's Nickname and other options can be changed using the Terminal Activity's command line Sugar-Control-Panel.
Changing the "XO Guy"
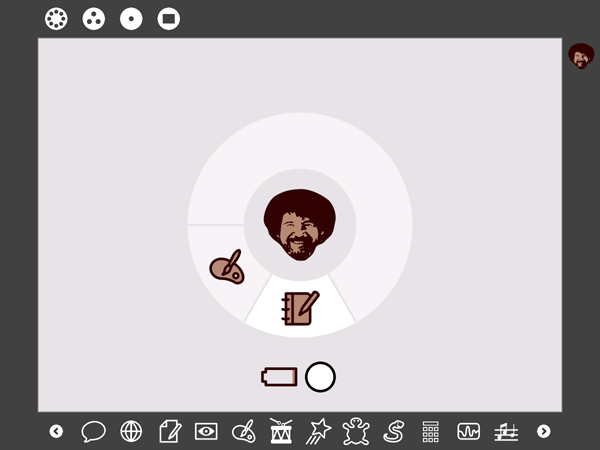
To change the XO Guy, the symbol in the middle of the Home view (with applications opening around him/her), you have to follow a few steps:
- Create An Icon - You first have to make an icon image and save it as an SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) file with the name computer-xo.svg. Probably on your Mac or Windows machine. There are instructions on how to do this on the OLPC wiki.
- Transfer It To Your Computer - Copy computer-xo.svg to a USB or SD card and plug it into your OLPC or computer.
- Install it - Open Terminal and type the following commands to back-up the original icon and copy your new icon into the correct location:
su -l cp /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg.bak cp /media/<your usb or sd>/computer-xo.svg /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg
- Now close terminal and press Ctrl,Alt,Erase.
Example of modified icon:
Restoring Icon To Original
To restore computer-xo.svg back to the original, open terminal and type:
su -l cp /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg.bak /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg rm /usr/share/icons/sugar/scalable/device/computer-xo.svg.bak
Source: http://olpcnews.com/forum/index.php?topic=2157.0
Setting the Clock and Timezone
You may set the date and time as follows:
- Connect to the Internet. (For details, see DocumentationTeam/User Manual/Connecting to the Internet)
- Open a Linux prompt. (For details, see How do I access a Linux command prompt? Note that unless you are an advanced user, you should use the Terminal Activity button to open the prompt.)
- Log in as "root". Assuming you are using the Terminal Activity program, you can log in as root by typing "su -" at the command prompt and pressing the Enter key. Note that as user "root" you have the ability to destroy all software on the XO, so you should end your session as soon as you successfully change the date and time.
- At the command prompt, enter the following commands:
/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov
/usr/sbin/hwclock --systohc - Press the Enter key after each. In response to the ntpdate command, if it successfully contacts this US government official time server, the system will output a line of data displaying the correct date and time.
- Click the "Stop" icon 25px at the upper right corner of the screen to log out and close the Terminal Activity program.
How to set the timezone on my laptop
You can set the timezone by typing the Sugar-Control-Panel command in the Terminal Activity.
Sound Control
Disabling the bootup sound
Turn the volume down while the laptop is booting (i.e. before getting into Sugar).
Taking Screen Shots
To take a screen shot, typing Alt+1 at the same time will take one and store it in your journal.
Networking & Communications
Connecting to Wireless Networks
To some degree, networking is specific to the platform upon which Sugar is running.
-
On the XO-1 laptop, there are three ways to connect to the Internet:
- Wireless access point (WiFi hotspot);
- “School Server” mesh network; or
- “simple” mesh network, which lets you collaborate directly with other XOs.
Read DocumentationTeam/User Manual/Connecting to the Internet for detailed instructions.
Connecting to Jabber Servers
Jabber servers allow Sugar users to interact, play and collaborate with each other in the Sugar environment.
While the OLPC is designed with mesh wireless networking built in (where users can connect to each other without having a central wireless internet router/connection), Sugar users around the world may not be able to connect with others using the platform unless it's through the Internet, since mesh networking relies on a concentration of users (for example, in a classroom, school or business environment).
Jabber networks link Sugar users to each other in order to chat, interact and collaborate. There are global Sugar Jabber networks, or regional ones hosted by organizations and individuals around the world. You can choose whichever Jabber network you wish to connect to. Connecting Sugar to one of these networks will greatly enhance your Sugar experience.
- Connecting to Jabber Networks - How to connect Sugar to a Jabber network
- List of Jabber Networks - Community/A list of Jabber networks around the world
- Creating a Jabber Server - To host a Jabber server for your city, region, country or interest read How to Create a Jabber Server
IRC Chat
Install the XoIRC activity and connect with other Sugar/OLPC users and enthusiasts on the internet and chat with them in real time. XoIRC uses a system called IRC.
It defaults to a "room" called #olpc-help, but you can also enter other rooms by typing /join #room where room is the name of the room you wish to join.
Some other Sugar/OLPC IRC chatrooms are listed here.
OLPC/Sugar as Webserver
- Open Terminal and type the following to install Boa (approx. 100k)
su - yum -y install boa
- Now put your index.html in /var/www
- Find your Sugar Computer/XO's IP Address. Still as root user (having entered su- already), enter into Terminal:
ifconfig
- Look next to eth0 for 192.168.whatever (for example)
- Go to another machine on your LAN and type your Sugar Computer/XO's IP Address into your browser. There's your Sugar computer serving up a web page!
Installing Sugar
- Installing Sugar (on various platforms)
- Sugar Instructions, booting and getting started with Sugar
Developing For Sugar
- Building the XO: Introducing Sugar - Red Hat Magazine 2007-02-23
- Build from sources, and get started.
- Read the human interaction guidelines
- Get an overview of the architecture
- Write your own activity
- Check out the code snippets library
- Understanding sugar code organization.
- See a list of Sugar activities and specifications.
- Sugar source repository
- Current trac tickets, sorted by category. The TODO list.
- Roadmap
See also
- DocumentationTeam/Glossary of Sugar terms