Activities/Turtle Art
What is Turtle Art
Where to get Turtle Art
There is a new experimental version of Turtle Art available: File:TurtleArt-83.xo.
Turtle Art is a fructose module, so it is included as part of the standard Sugar (sucrose) distribution.
Version 82 | addons | Source | FLOSS Manual | laptop.org Turtle Art page | Student Guide | activity guides (es) mas TortugaArte | Experimental fork | Turtle Art Gallery | 0.86 release notes | Introductory video | Sugar Labs tickets | OLPC tickets | Another Turtle Art gallery
Note: The first time you run Turtle Art, it takes about 60 seconds to load. You'll see a mostly blank screen after the initial flashing of the icon. Subsequently, the loading time is ~5 seconds (on an OLPC-XO-1 laptop).
i18n
Turtle Art currently has support for: de, el, en, es, fi, fr, it, mn, nl, pt, ru, sl, sv, ta, tr, vi, and zh_TW
(See our Pootle server for details about how to translate Turtle Art into your language.)
Background
Turtle Art is an activity with a Logo-inspired graphical "turtle" that draws colorful art based on Scratch-like snap-together visual programming elements.
Turtle Art is intended to be a stepping stone to the Logo programming language, but there are many restrictions compared to Logo. (Only numeric global variables and stack items are available, no lists or other data-structures. The conditionals and some of the functions only take constants or variables, not expressions. Limited screen real-estate makes building large programs unfeasible.) However, you can export your Turtle Art creations to Berkeley Logo. The experimental version of Turtle Art also has a (limited) facility for sensor input, so, for example, you can move the Turtle based upon sound volume or pitch.
A portfolio feature lets you use Turtle Art to create multimedia slide shows from material retrieved from your Journal. The basic idea is to import images (and eventually movies, audio, and text files) into slide templates, not unlike Powerpoint, and then show a presentation by stepping through them. The portfolio includes the typical major functions of presentation software: an editor that allows text to be inserted and formatted (this is largely incomplete), a method for inserting images (from the Journal), and a slide-show system to display the content. What makes it a bit different than tools such as Powerpoint is that you can program your slides using Turtle Art blocks. Turtle Art also has an export-to-HTML function so that presentations can be viewed outside of the Sugar environment.
Turtle Art was written by Brian Silverman and is maintained by Walter Bender. Arjun Sarwal added the sensor features. Luis Michelena contributed to the "named" action and box blocks. Tony Forster has been the lead test engineer and has really stretched the boundaries of Turtle Art.
Learning with Turtle Art
Play with Turtle Art to draw colorful art patterns using a turtle that accepts instructions for movement.
With visual programming blocks, you can snap together programs by compiling (combining) them in ways to create anything you can imagine.
maths
A clock activity
Calculating the hypotenuse and approximating the angle of a right triangle; Stepping through the program is a nice way to visualize the process of approximation; The final result of the approximation.
And on-the-fly function definitions:
Tony Forster describes his "adventures" with on-the-fly definitions to create an analog clock in his blog.
Try any of the time or math library functions, e.g.,
localtime().tm_min
sin(x) + sin(pi/2)
presentations
games
Turtle Art can be used to write games, such as a simple falling block game:
Portfolios
In the era of high-stakes testing, we have the means to measure “which child knows more”; these data tell us about relative merit of the school in which a child is enrolled. The Turtle Art portfolio feature is an assessment tool that shows “what a child knows”; children become the curators of their own work. They advance their own learning and help their teachers, parents, and school administrators understand better the depth and breadth of what they have learned.
A recent article in the Chronicle of Higher Education claims:
- ePortfolios can integrate student learning in an expanded range of media, literacies, and viable intellectual work;
- ePortfolios enable students to link together diverse parts of their learning including the formal and informal curriculum;
- ePortfolios engage students with their learning;
- ePortfolios offer colleges a meaningful mechanism for accessing and organizing the evidence of student learning.
Turtle Art portfolios engage children in the process of reflecting on their work—what they have done, how they have done it, and how success these efforts have been—as they create a multimedia narrative to show their teachers, parents and peers what they have learned. Turtle Art Portfolio builds upon the journaling functionality of the Sugar learning platform, where every action or activity a child takes in the classroom is automatically recorded in a folder: (1) by enabling the child to select important learning achievements, be they in reading, writing, arithmetic, arts, music, physical education, history and social science, etc. Children answer questions such as “I chose this piece because...” (2) creating a multimedia narrative presentation from their selections (including audio voice-overs and video), reflective of the multiple ways in which children learn; and (3) sharing their presentation with classmates, both to celebrate what they have learned, but also to engage in a critical dialog about their work.
Turtle Art portfolio is innovative in three ways: (1) it builds upon a journal of *all* learning activities that is automatically collected; (2) it has unique programmability, fun and accessible to even the youngest elementary school children, but interesting and engaging to middle-school children as well; and (3) it has unique tools for both collaborating on the construction of the portfolio and its subsequent sharing with others.
Portfolios have been shown to be “a powerful means for children to assess their own work, set goals, and take responsibility for their future learning.” But portfolio assessment has seen limited applicability. It is a practical, engaging means to using portfolios. By building upon the automatic accumulation of work in journal (including a “screen capture” of their work) the portfolio process can readily be integrated into the classroom routine. Reflection becomes the norm: children are encouraged write in their journals (young children record audio notes) for a few minutes after *every* class. The numbing question, “what did you do in school today?” need no longer a necessary part of the parent-child dialog. Instead, the parent can talk to the child about actual artifacts.
Culling from the journal becomes part of the end-of-term assessment process. The process of telling one's story as a learning requires further reflection. At a “portfolio social”, parents are invited to view presentations and ask children about their learning; the child's voice is heard.
The classroom teacher can add addition assessment slides to the portfolio about themes such as work habits and personal growth, as part of an archive that travels with a child across grade levels. Through juxtaposition, the child and teacher can see what has changed over the course of the years, trends, and areas for improvement, Also, a classroom portfolio can be assembled as part of a teacher-assessment process.
Some additional background on ePortfolios can be found here:
Getting Started
Start by clicking on (or dragging) blocks from the Turtle palette. Use multiple blocks to create drawings; as the turtle moves under your control, colorful lines are drawn.
You add blocks to your program by clicking on or dragging them from the palette to the main area. You can delete a block by dragging it back onto the palette. Click anywhere on a "stack" of blocks to start executing that stack or by clicking in the Rabbit (fast) or Turtle (slow) buttons on the Project Toolbar.
tips
Did you know that you can copy/paste stacks to/from the clipboard? You type Ctrl-C to copy whatever stack is under the cursor to the clipboard. Ctrl-V will paste from the clipboard onto whatever TA project you have open. Try pasting this code into your Turtle Art project.
- [[0, "hat2", 880, 80, [null, 1]], [1, "forever", 892, 130, [0, 2, null]], [2, "kbinput", 973, 144, [1, 3]], [3, "if", 973, 198, [2, 4, 7, 8]], [4, "greater", 1053, 208, [3, 5, 6, null]], [5, "keyboard", 1085, 217, [4, null]], [6, ["number", "0"], 1234, 217, [4, null]], [7, "stopstack", 1068, 272, [3, null]], [8, "wait", 973, 313, [3, 9, null]], [9, ["number", "0.5"], 1047, 322, [8, null]]]
You can also paste text from the clipboard into text blocks.
Turtle Art runs in Sugar and in the GNOME desktop.
Video Tutorials
I know there are a few but they are not categorized on this page... we'll make that happen soon. Help would be appreciated.
- introductory videos here on Turtle Art
- To Square—a tutorial by the Summer Spot youths at the Lilla G. Frederick Pilot Middle School
- A basic tutorial.
- a video of the portfolio basics
- Get your hot cold Turtle Art Video here!
- Name that State!
- A Shapes and Colors Game
Main Toolbar
From left to right: Activity toolbar; Edit toolbar; View toolbar; show/hide palette; erase canvas; run project fast; run project slow; stop project; Help toolbar; stop activity
Keyboard short cuts for the above: Alt+ palette; blocks; run; walk; stop; erase; e.g., Alt+e will erase the screen. Esc will return from full-screen mode.
Notes: The run buttons are tied to the Start Block. If no Start Block is used, then all blocks are run when either run button is clicked. The "rabbit" button runs the blocks at maximum speed. The "turtle" button pauses and displays the turtle between each step. The "bug" button pauses between each step and shows status information.
Project Toolbar
Project title; share button; keep button; save copy to Journal button; save to HTML; save to Logo; save as an image; import Python code; import Turtle Art project
Edit Toolbar
The Edit toolbar is used to copy stacks of blocks to the clipboard and to paste stacks from the clipboard. To copy a stack, place the cursor on any block in the stack and then type Ctrl-c. To paste a stack from the clipboard, type Ctrl-v.
View Toolbar
Hide/show blocks; full-screen button; Cartesian-coordinate grid; polar-coordinate grid; display of x,y coordinates of turtle; rescale-coordinates button; grow block size; shrink block size
Help Toolbar
Import sample project; display help strings
Palettes Toolbar
There are eight palettes of program elements available for program construction: Turtle movements; Pen attributes; Color attributes; Numeric operators; Misc. functions; Logical operators; Logical blocks; and Presentation blocks
On the far-right end of the toolbar is the hide/show palette button.
Blocks are dragged from the palette onto the canvas surface. To dispose of a block, drag it back onto the palette.
The palettes can be displayed horizontally or vertically (See below). Orientation is adjusted by clicking on the and buttons on the upper-left corner of the palette. The palette can be hidden by clicking on the button on the lower-right corner of the palette. The next palette in the menu can be accessed by clicking on the button on the upper-right corner of the palette.
These blocks are used to control the movements of the turtle.
These blocks are used to control the attributes of the turtle's pen.
These blocks can be used with the set-pen-color block.
These blocks are arithmetic and boolean operators.
These blocks control program flow.
These blocks are for defining variables and subroutines.
These are a collection of extra blocks for accessing advanced features.
These blocks are used to make multimedia presentations.
An example of a vertical palette.
Quick Tutorial on using the portfolio features
A video of the portfolio basics is available here.
A PDF of a Turtle Art portfolio presentation can be downloaded File:Desktop-Summit.pdf.
Sharing
Turtle Art supports a simple sharing model. Whomever joins a shared activity will get a copy of the current state of the project from the initiator of the share. Subsequent changes to the project are shared between all participants. It is not recommended to share among more than 2–3 people at a time. Please note that if different versions of Turtle Art are used in the same share instance, there may be problems, as old versions won't know how to handle new bricks introduced in later versions.
Exporting to Berkeley Logo
Turtle Art can export its projects to Berkeley Logo (using the Save as Logo button on the Project Toolbar)
Note: The project is saved to the Journal as "logosession.lg". UCB Logo does not yet access the Journal directly, so it is necessary to copy the project out of the Journal using the "copy-from-journal" command in the Terminal Activity and then accessing the project using the File menu within the UCB Logo Activity.
copy-from-journal logosession.lg
Internals
Some procedures for setting up the palette and the shade functionality:
to tasetpalette :i :r :g :b :myshade make "s ((:myshade - 50) / 50) ifelse lessp :s 0 [ make "s (1 + (:s *0.8)) make "r (:r * :s) make "g (:g * :s) make "b (:b * :s) ] [ make "s (:s * 0.9) make "r (:r + ((100-:r) * :s)) make "g (:g + ((100-:g) * :s)) make "b (:b + ((100-:b) * :s)) ] setpalette :i (list :r :g :b) end
to rgb :myi :mycolors :myshade make "myr first :mycolors make "mycolors butfirst :mycolors make "myg first :mycolors make "mycolors butfirst :mycolors make "myb first :mycolors make "mycolors butfirst :mycolors tasetpalette :myi :myr :myg :myb :myshade output :mycolors end
to processcolor :mycolors :myshade if emptyp :mycolors [stop] make "i :i + 1 processcolor (rgb :i :mycolors :myshade) :myshade end
to tasetshade :shade make "myshade modulo :shade 200 if greaterp :myshade 99 [make "myshade (199-:myshade)] make "i 7 make "mycolors :colors processcolor :mycolors :myshade end
to tasetpencolor :c make "color modulo round :c 100 setpencolor :color + 8 end
make "colors [ 100 0 0 100 5 0 100 10 0 100 15 0 100 20 0 100 25 0 100 30 0 100 35 0 100 40 0 100 45 0 100 50 0 100 55 0 100 60 0 100 65 0 100 70 0 100 75 0 100 80 0 100 85 0 100 90 0 100 95 0 100 100 0 90 100 0 80 100 0 70 100 0 60 100 0 50 100 0 40 100 0 30 100 0 20 100 0 10 100 0 0 100 0 0 100 5 0 100 10 0 100 15 0 100 20 0 100 25 0 100 30 0 100 35 0 100 40 0 100 45 0 100 50 0 100 55 0 100 60 0 100 65 0 100 70 0 100 75 0 100 80 0 100 85 0 100 90 0 100 95 0 100 100 0 95 100 0 90 100 0 85 100 0 80 100 0 75 100 0 70 100 0 65 100 0 60 100 0 55 100 0 50 100 0 45 100 0 40 100 0 35 100 0 30 100 0 25 100 0 20 100 0 15 100 0 10 100 0 5 100 0 0 100 5 0 100 10 0 100 15 0 100 20 0 100 25 0 100 30 0 100 35 0 100 40 0 100 45 0 100 50 0 100 55 0 100 60 0 100 65 0 100 70 0 100 75 0 100 80 0 100 85 0 100 90 0 100 95 0 100 100 0 100 100 0 90 100 0 80 100 0 70 100 0 60 100 0 50 100 0 40 100 0 30 100 0 20 100 0 10] make "shade 50 tasetshade :shade
to tasetbackground :color :shade tasetshade :shade setbackground :color + 8 end
The project:
to ta clearscreen tasetbackground 21 100 setpensize 25.0 make "box1 0.0 repeat 300.0 [ tasetpencolor xcor / 6.0 tasetshade heading forward :box1 right 91.0 make "box1 :box1 + 1.0 ] end
ta
Looking under the hood
Turtle Art projects are stored as two files: (1) a .ta file contains a json-encoded serialization of the project; and (2) a .png file of the canvas.
The json encoding of a repeat 4 forward 100 right 90 project:
[[0,"repeat",331,158,[null,1,2,null]],[1,["number","4"],417,167,[0,null]],[2,"forward",426,207,[0,3,4]],[3,["number","100"],500,216,[2,null]],[4,"right",426,246,[2,5,null]],[5,["number","90"],500,255,[4,null]],[-1,"turtle",0,0,0,0,50,5]]
Programmable Brick
The following feature is only available in versions 44+ of Turtle Art.
myblock.py
And a block that can be programmed by the Pippy interface:
A copy of the tamyblock.py module is stored in the Journal when you first launch Turtle Art. You can edit the module in Pippy and then import your custom code into Turtle Art using the Pippy button.
To use the customized block, select the "view source" block from the Sensors palette.
Examples:
def myblock(lc,x):
# draw a dotted line of length x
# make sure x is a number
if type(x) != int and type(x) != float:
return
dist = 0
# save current turtle pen state
pen = lc.tw.turtle.pendown
# repeat drawing dots
while dist+lc.tw.turtle.pensize < x:
setpen(lc.tw.turtle, True)
forward(lc.tw.turtle, 1)
setpen(lc.tw.turtle, False)
forward(lc.tw.turtle, (lc.tw.turtle.pensize*2)-1)
dist += (lc.tw.turtle.pensize*2)
# make sure we have moved exactly x
forward(lc.tw.turtle, x-dist)
# restore pen state
setpen(lc.tw.turtle, pen)
return
def myblock(lc,x):
# push an uppercase version of a string onto the heap
if type(x) != str:
X = str(x).upper()
else:
X = x.upper()
# push result onto heap (use the pop block to use the new string)
lc.heap.append(X)
return
def myblock(lc,x): # push hours, minutes, seconds onto the heap # use three pop blocks to retrieve the values # remember: the heap is a FILO (first in, last out) # the first value you will pop will be seconds lc.heap.append(localtime().tm_hour) lc.heap.append(localtime().tm_min) lc.heap.append(localtime().tm_sec) return
def myblock(lc,x):
# add a third dimension (gray) to the color model
# calculate the value (brightness) of the current color
val = 0.3 * lc.tw.rgb[0] + 0.6 * lc.tw.rgb[1] + 0.1 * lc.tw.rgb[2]
# make sure gray is in range from 0 to 100
if x != 100:
x = int(x)%100
# mix in gray
r = int((val*(100-x) + lc.tw.rgb[0]*x)/100)
g = int((val*(100-x) + lc.tw.rgb[1]*x)/100)
b = int((val*(100-x) + lc.tw.rgb[2]*x)/100)
# reallocate current color
lc.tw.fgcolor = lc.tw.cm.alloc_color(r<<8,g<<8,b<<8)
return
def myblock(lc,x) # save a screenshot in the journal lc.tw.activity._do_saveimage_cb(lc.tw.activity) return
From the field
Tony Forster has written a number of blog posts about his experiments with Turtle Art: Using Python blocks in TurtleArt Turtle Lander Reprogramming Sugar Turtle random Turtle random V2 Turtle Lissajous Turtle spring damper color and shade Turtle Art shapes Bouncing Turtle Turtle Pythagoras Turtle graph Turtle Pi Turtle fractions Turtle interactive multimedia
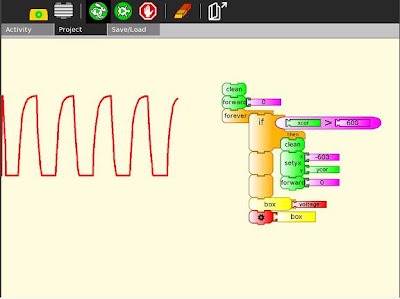
An bringing it all together, the Turtle Art Oscilloscope.
Tony has also used the programmable block to do file IO.
Just for fun
Using Turtle Art for pie charts
Q: How do I cast keyboard input to a string? Looking at the source your are using ord() to fetch the input... is there a way to convert that back to string before showing it? ANS: Use chr(). See the example in the illustration.