Supported systems: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
update Mandriva |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
|[[Image:Alt_linux_team_small.png|36px]]ALT Linux||4.1<br>Sisyphus||0.82.1<br>0.83.5||Yes|||| || [[Community/Distributions/ALTLinux | Sugar on ALT Linux]] | |[[Image:Alt_linux_team_small.png|36px]]ALT Linux||4.1<br>Sisyphus||0.82.1<br>0.83.5||Yes|||| || [[Community/Distributions/ALTLinux | Sugar on ALT Linux]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:mandriva.png|36px]]Mandriva||Cooker||0. | |[[Image:mandriva.png|36px]]Mandriva||Cooker||SugarPlatform-0.84.0||Yes|||| ||[[Community/Distributions/Mandriva | Sugar on Mandriva]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Caixa Mágica.png|36px]]Caixa Mágica||12||0.83.5||Yes|| || || [[Community/Distributions/Magalhães | Sugar on Magalhães]] | |[[Image:Caixa Mágica.png|36px]]Caixa Mágica||12||0.83.5||Yes|| || || [[Community/Distributions/Magalhães | Sugar on Magalhães]] | ||
Revision as of 05:13, 16 March 2009
me
</noinclude>
Are you new to Sugar?
There are two Live Systems that run Sugar from a USB stick or bootable DVD:
- Sugar on a Stick based on Fedora, runs on 64-bit PCs and OS/X Macintoshes, OLPC XO and Raspberry Pi, in English only
- Trisquel On A Sugar Toast, runs on 32- and 64-bit PCs and has more Activities and world language support
If you have a high-speed Internet connection, Fedora with the Sugar graphical learning environment may be installed to a hard disk or a a 4 GB USB stick with a Netinstall CD
Do you use GNU/Linux?
Sugar is supported by several GNU/Linux distributions. Sugar Labs does not support any specific distribution, but does focus development on Fedora and Debian, which helps SoaS and Ubuntu.
| Logo | Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar on a Stick | Live system of the Sugar Learning Environment | |
| Fedora | Fedora 34 | |
| Ubuntu | Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic | |
| Debian | Debian Stretch, see also Live Build | |
 |
OLPC OS 16.04 | OLPC OS for OLPC NL3 laptops based on Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial |
 |
OLPC OS 13.x | OLPC OS for OLPC XO laptops based on Fedora 18 |
| openSUSE | Part of an Linux for Education (Li-f-e) series | |
| Trisquel Toast | Based on Ubuntu |
Are you a developer?

|
Please see this developer documentation website for the sugar-build development environment.
|
Virtual Machines on all platforms
 |
VirtualBox Appliances |
|
|
If you run into problems, you may want to consult the Talk:VirtualBox page for help.
Are you preparing a deployment without Internet access?
 |
See Sugar Creation Kit |
Are you looking for Sugar Activities?
| Visit the Sugar Activity Library | <imagemap>
File:Sugarlabs_mainpage_02.png rect 14 14 38 47 Calculate rect 74 15 107 44 Chat rect 137 16 171 43 Implode rect 201 14 238 46 Distance rect 265 12 298 47 Etoys rect 11 79 41 108 Moon rect 74 78 106 110 Paint rect 140 78 170 109 Pippy rect 201 80 235 108 Read rect 266 82 298 107 Record rect 11 143 41 172 TamTam Synth Lab rect 75 146 105 169 Terminal rect 142 140 166 173 Turtle Blocks rect 201 144 235 171 WikiBrowse rect 269 142 299 173 Write default Sugar Activity Library desc none </imagemap> |
Page Index
Sugar is implemented on top of existing or modified operating systems and hardware. Sugar Activities ("Sugarized applications") are accessed by the user in the Sugar platform, integrated into a single Journal for storage, and are often designed with peer collaboration as a primary feature.
| Journal Content |
meta-tagged content datastore | |||||||
| Sugar Activities |
Browse | Chat | Read | Write | Record | EToys | Turtle Art | Terminal | et al... | |||||||
| Sugar Platform |
Sugar Platform Stack: Sugar Framework and Sugar Software Stack | |||||||
| Operating System |
Fedora | Debian | Ubuntu | Linux, other | LTSP | Mac OSX | MS Windows (emulation) | ... | |||||||
| Hardware Platform |
OLPC XO-1 |
ASUS EEE PC |
Intel Classmate |
OLPC XO-2 |
... | |||
The layers in a Sugar system are:
- Journal
- Activities
- Sugar Platform Stack
- Operating System
- Computer Hardware
Sugar System Stack (ASCII Text)
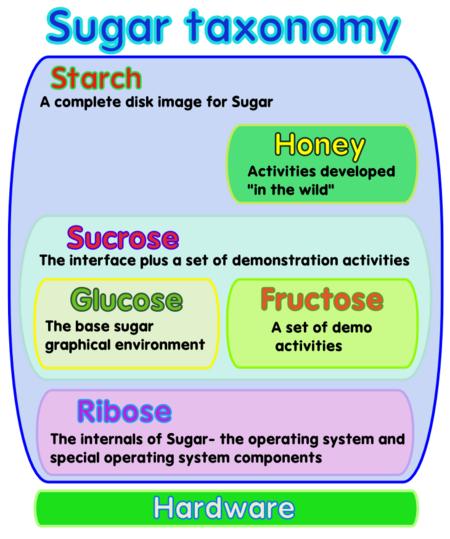
Sugar Labs has borrowed names from carbohydrate chemistry, which includes sugar, to personalize and help distinguish pieces of Sugar software. See Taxonomy and On the Naming of Sugar for background.
System Stack Illustration
Two steps
- Determine which of the various methods of running Sugar meet your needs:
- Pre-installed Sugar:
- Some computers come with Sugar pre-installed, most notably the OLPC-XO-1 laptop.
- LiveCD/LiveUSB:
- Suitable for trying Sugar without having to install any software on almost any computer—just boot Sugar off of a CD or USB drive. For USB Solutions goto our Sugar on a Stick project page.
- Install Sugar:
- If you are running one of the currently supported distributions, you can install Sugar using your systems standard package manager, e.g., Synaptic, apt-get, or yum.
- Emulator:
- QEMU or VMWare let you run Sugar in an emulator on your computer—you'll need to install an emulator from which you launch Sugar.
- Pre-installed Sugar:
- Refer to the matrix below to find a Sugar solution that works for you.
Computer labs
- Bill Kerr has written up instructions for trying Sugar in computer labs which run only Windows
- (Please see [1].)
- Caroline Meeks is developing a deployment model that only requires one USB stick per child. (Please see Sugar on a Stick.)
Matrix of Sugar solutions
There are many ways to run Sugar:
- As a complete disk image on an existing machine;
- As a session on a Linux system; or
- As part of a complete hardware-software platform.
Supported systems/Technical considerations
- A discussion of technical considerations regarding supported systems.
Starch
Starch is a complete disk image for Sugar.
| Name | Sugar Version | Tested | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar on a Stick | 0.84 | In process | This is a Live USB of the Sugar, and one of the primary focuses of Sugar development. |
| LiveBackup XO-LiveCD | 0.82 | No | This is a Live CD of the OLPC system. Release Notes |
| Sugar on a Stick is a Fedora Live USB. There is also Fedora "Rawhide" on XO development. | |||
| 0.82 | Instructions for installing a Ubuntu LiveUSB |
Sucrose
Sucrose is the Sugar interface plus a set of demonstration activities.
| Operating System | Version | Sugar Version | Bundled | Tested | Collaboration Links | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary packages available | ||||||
| 4.0 | 0.82 | Yes | Yes | Sugar on Debian | ||
| 7,8,9 | 0.82 | Yes | Yes | Sugar on Fedora | ||
| 8.04 (Hardy) | 0.79.0-0ubuntu3 | Yes | Yes | http://wiki.ubuntu.com/SugarTeam | Sugar on Ubuntu | |
| 8.10 (Intrepid) | 0.82 | Yes | Sugar on Ubuntu | |||
| 4.1 Sisyphus |
0.82.1 0.83.5 |
Yes | Sugar on ALT Linux | |||
| Cooker | SugarPlatform-0.84.0 | Yes | Sugar on Mandriva | |||
| 12 | 0.83.5 | Yes | Sugar on Magalhães | |||
| packages not pre-built | ||||||
| 2009-02-15 | 0.83.6 9999 |
Yes | Sugar on Gentoo | |||
| 11.1 | 0.84 | Yes | http://en.opensuse.org/Sugar IRC Freenode #opensuse-edu |
Sugar on OpenSUSE] | ||
| Sugar on a Mac (in emulation) | ||||||
| Slackware 12 | Sugar on Slackware | |||||
| WindowsXP | No | Sugar on Windows (using QEMU) | ||||
Sugar for various hardware systems
Since Sugar is now available on most major GNU/Linux distributions, it is possible to run Sugar almost any computer that can run GNU/Linux. We highlight some systems below. Please add your favorite to the list.
| Manufacturer | Model | Operating System | Tested | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLPC | XO-1 | Fedora 9 | Yes | Standard (reference) distribution |
| ASUSTeK | Eee PC | In initial testing phase | ||
| Intel | Classmate Gen 1 & Gen 2 | under development |
Getting the Sugar sources
Distributors can find the latest sources for the sucrose components here. Each sucrose roadmap entry has as well links to the release pages of earlier releases.
Updating Sugar to the Latest Version
Ubuntu
For a LiveCD/LiveUSB, check out the instructions [2].
Updated sucrose packages are usually published in a PPA: See here for details.
If you want up-to-the-minute freshness (and brokenness) you can use jhbuild to build from source instead of the released packages. Follow the instructions here to install sugar-jhbuild as an xsession option.
Debian
Sucrose packages are usually updated in unstable. These packages migrate to testing after a while. You can see the current package versions here.
If you want up-to-the-minute freshness (and brokenness) you can use jhbuild to build from source instead of the released packages.
Fedora
Fedora LiveCD/Live USB
- Project page: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Sugar_Spin
With this spin, you'll be able to run Sugar, which is developed by Sugarlabs and the desktop environment used on the OLPC, directly from a Live CD! You'll find several activities on the image including most notably...
- sugar-browse - a web browsing activity based on xulrunner
- sugar-write - a word processor based on abiword
...along with several other activities including Chat support.
- See our Sugar on a Stick page.
The Fedora OLPC SIG, https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/OLPC, will be importing further activities into Fedora, which might be installed using yum install sugar-* at a later time.
- Recent development spins:
For more information, please refer to the announcement here:
https://www.redhat.com/archives/fedora-olpc-list/2008-December/msg00061.html
What if you wanted to put it quickly onto your USB Key? You'll just need to grab Luke Macken's liveusb-creator, which already includes support for the Sugar Spin. Here's the link:
The liveusb-creator still contains an old link, which is the reason why you'll need to download the spin manually until this gets fixed.
Tip of the hat: Sebastian Dziallas and the Fedora team
Fedora on an OLPC XO
On an OLPC XO-1 laptop, run olpc-update as root.
Normally you only need to run olpc-update in the Terminal application with a build number, like this:
# sudo olpc-update 767
Note: Now you can do this by means of the graphical Sugar Control Panel.
OLPC Clean Install
http://wiki.laptop.org/go/Clean-install_procedure
Update to the latest experimental version (a.k.a. Joyride)
Joyride is for developers; it is not supported. Joyride builds may cause data corruption and in rare cases, even cause hardware damage, so please do not use Joyride on mission-critical systems.
Joyride contains all the "bleeding-edge" features that are being debugged for inclusion in the next release.
Open the Terminal application and type the following, substituting 2469 for the latest version number.
# olpc-update joyride-2469
What's the latest version? You can find the latest build number (shown above as 1779) at the bottom of http://xs-dev.laptop.org/~cscott/xo-1/streams/joyride/
Updates usually takes 10–15 minutes. It's advised that you plug your XO in while Sugar updates itself, then reboot it to see the new OS take effect.
Other Options
These are options that can be used with the update command:
# olpc-update --help
Usage:
olpc-update [options] --hints hints-file
olpc-update [options] [-rf] build-number
olpc-update [options] [-rf] --usb
olpc-update --version
olpc-update --help
For example:
olpc-update 630
olpc-update joyride-1779
olpc-update update.1-700
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f, --full skip incremental update attempt.
--force force update to an unsigned build.
-r, --reboot reboot after a successful update.
--hints=FILE name of json-encoded hints dictionary identifying the desired
new version.
-u, --usb upgrade from new build on inserted USB stick.
-v display verbose progress information; repeat for more verbose
output.
-q, --quiet don't output anything; use exit status to indicate success.
--version display version and license information.
Gentoo
- There are two methods to get Sugar on your Gentoo box: sugar-jhbuild and Sugar overlay. See Gentoo for details.
ALT Linux
- ALT Linux Team is an international software developers team, collectively working on Sisyphus.
- To install Sugar try these packages.
Mandriva
To install Sugar on Mandriva follow these instructions.






