Activity/Gogo
Introduction
From the GoGo website [1]...
The GoGo board is a programmable device that is designed for sensor-based and control projects. It is suited for building robots, data loggers, and devices for human-computer interaction. Its functionality is inspired by the MIT Cricket and many other programmable devices such as the the Lego Mindstorms, the IRX board, and Basic Stamps.
The GoGo Activity is a Python version of the "Monitor" program (MS Windows) and builds upon the Br-GoGo project code [2]. Effort is under way to replicate most of the functionality of the original program and extend/improve certain areas. At the moment this XO version should be considered "Sugar-coated" rather than "Sugar-ized". The integrated nature of the program means breaking it down into distinct activities would detract from fluid navigation. However there are certain elements which could benefit from Sugar's Sharing and Journalling features and these will be addressed in time.
Please see the sites listed under "Further Information" for GoGo-Board help and documentation. The main purpose of this Wiki page is to help you get started, familiarise you with the use of the GoGo-Board on the XO, specifically with the GoGo Activity and any issues you may encounter. Several other websites are listed at the end of this page, such as the SugarLab "Bugs" page which is where problems and feature requests should be submitted.
Work continues on the GoGo Activity so please check back soon for news of new features.
Quick Tour
Install & Launch
Installation is performed on the XO clicking the "download" button on the GoGo Activity Web Page. The activity can be identified by the ingeniously imaginative icon shown below. This icon should be on your home-screen straight after installation. If not then check for it in the "list-view" mode of the home-screen and click the star on the left to have the icon displayed on the Favorites-view. If GoGo is no where to be found then some older XO/OS's require that Sugar be restarted using ctrl-alt-erase.
NOTE: POWER-SAVING IS DISABLED WHILE GOGO IS RUNNING!!! The GoGo-Board is a USB-connected device and, unless you use batteries, loses power and disconnects when the XO enters power-saving mode. This can be inconvenient so power-saving is temporarily disabled while the activity is running but returned to previous state on exiting. Methods to avoid disabling power-saving or limit it's use are under discussion.

Connection Tab: Plug In, Switch On & Connect!
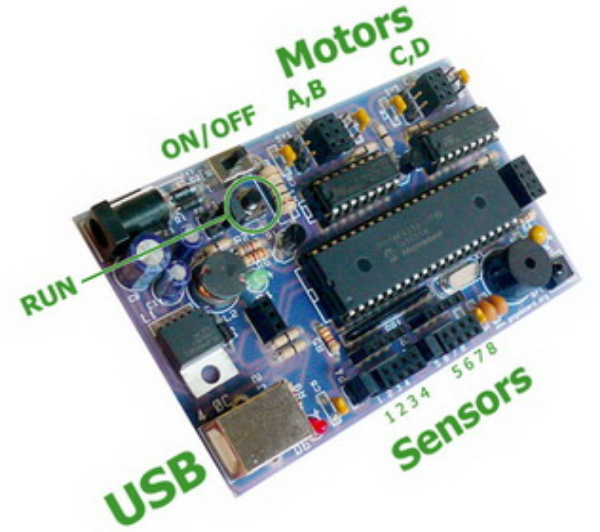
The following image provides an overview of the GoGo-Board itself. Take particular note of the On/Off switch, the green LED (left-center), the red LED next to the USB connector, the beeper (round thing on the right) and a programmable LED near it. All of these are useful for diagnosing connection problems, as described below.
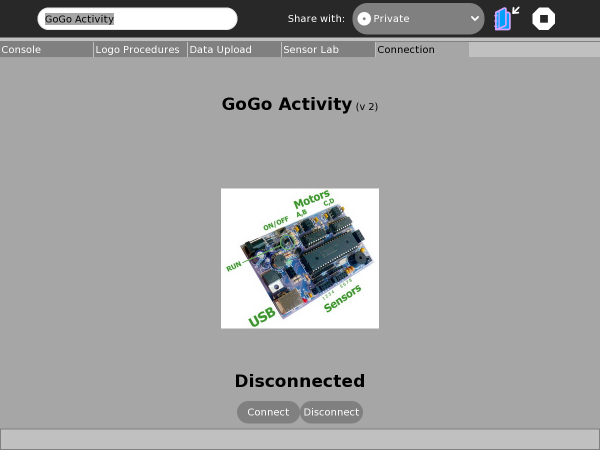
On starting the GoGo activity the Console-Tab is displayed as shown below. In the top of the central region is the name and version of the activity. Please quote the version number if you encounter any problems. In the center is the image of the GoGo-Board itself, which will be larger is the next version. Below that is the current status "GoGo Connected"/"GoGo Disconnected" followed by "Connect"/"Disconnect" buttons. Also note the status-bar at the bottom of the screen which displays (sometimes transient) messages.
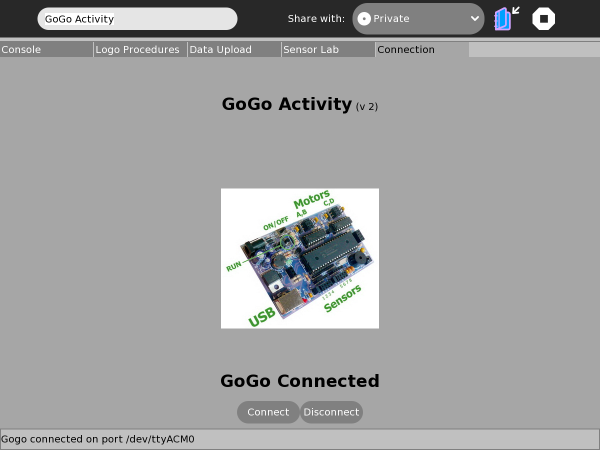
The board should be plugged in switched on before clicking the "Connect" button. When the board is switched on the green LED lights up, the beeper beeps and the programmable LED flashes a couple of times. When clicking the "Connect" button watch out for the red LED near the USB connector, which should flash when the XO and GoGo-Board communicate. If the red LED does not flash then the GoGo activity will have failed to connect and you should consult the "Failing To Connect" section on this page. All being well the connection status should show "GoGo Connected" along with the port being used in the status-bar, as shown below:
Console Tab: Control & Monitor
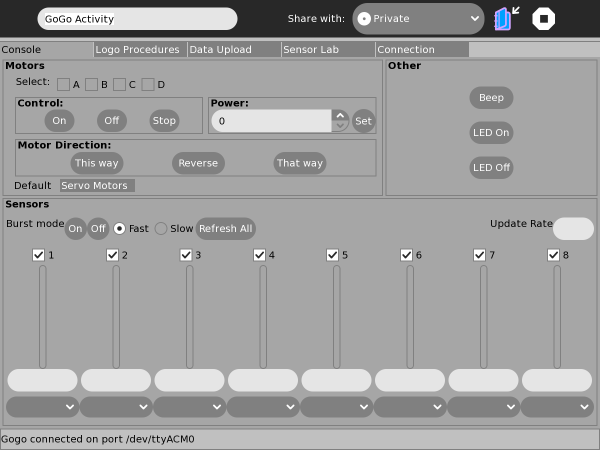
The Console Tab allows you to directly control motors & servo's, the programmable LED, the beeper and to monitor GoGo connected sensors. In the image below the upper left section is for controlling motors and servo's. Note that this is a tabbed-section (with the tabs at the bottom) for selecting between Motors/Servo's. Also note that only those selected in the group of check-boxes denoted A/B/C/D will be effected. The lower section allows one-shot or continuous sensor monitoring and each sensor "type" can be selected from the drop-down boxes at the bottom. The available sensors-types is dictated by those listed in the "Sensor-Lab" tab, detailed later.
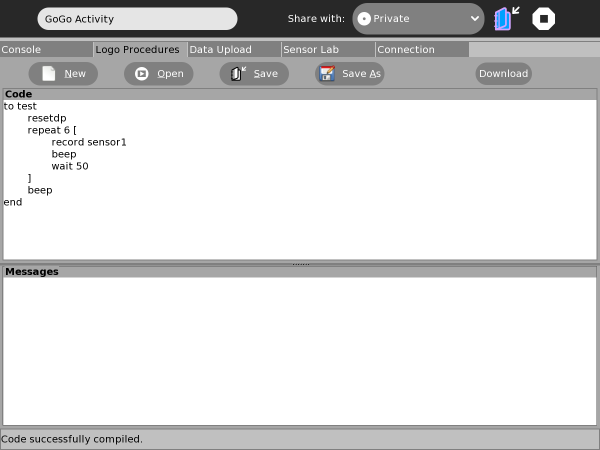
Logo Procedures Tab: On-board Programs
The GoGo-Board can store compiled Logo code which can be run by clicking the board's "run" button. Stored code can be run with/ without the board being connected to the XO (batteries or alternative power source are required when the board is untethered). Code is created, edited, saved, loaded and "uploaded" via the Logo Procedures tab shown in the image below. Code is compiled and uploaded (if no errors) in a single step when the "Upload" button is clicked. The "Messages" section will report any errors in the Logo code, in which case nothing should actually be uploaded to the board.
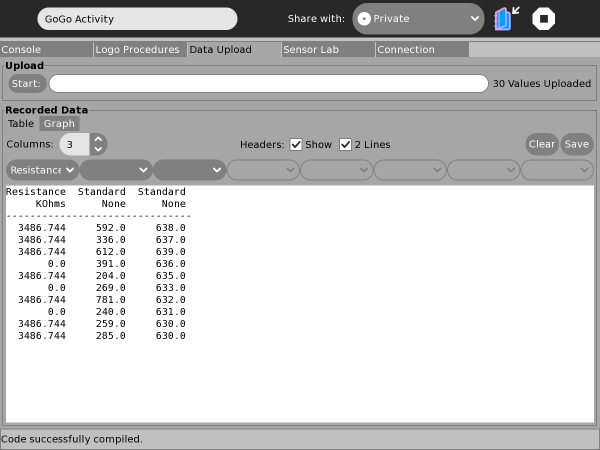
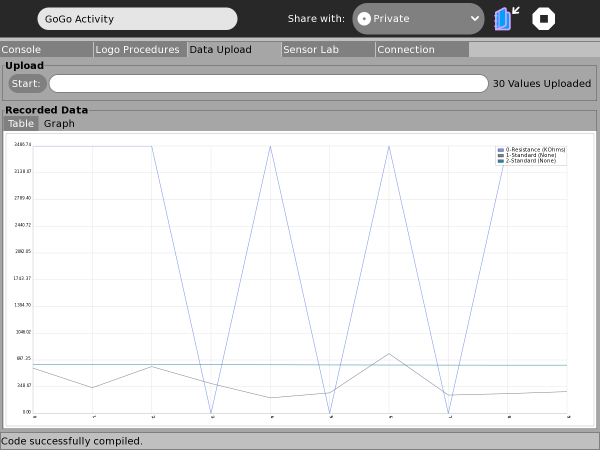
Data Upload Tab: Capture, Graph & Save
Logo procedures can include commands to capture data, storing it on-board until
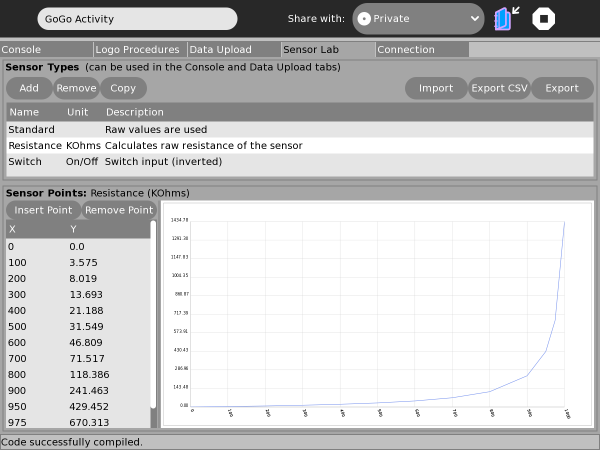
Sensor-Lab Tab: Calibration Data
Sensor values, even for switches, fall in the range 0..1023. The Sensor-Lab is where particular sensor "types" can be created to calibrate these values, give more meaningful names and specify the units used (eg, Resistance, KOhms). Calibration data is defined by specifying a number of calibration "points" between which the application will interpolate to convert the raw sensor values. In this way a library can be created of commonly encountered sensor types and their calibration data can be assigned when monitoring sensors in the Console tab and when importing captured data in the "Data Upload" tab. In the image below you can see the list of sensors, the calibration points for the selected sensor and a (slightly rough) idea of the shape of the calibration curve in the graph. For easier creation and editing of calibration data the information for each sensor can be exported and imported in both Comma-Separated-Variables (CSV) format or custom "Sensor" format. Like-wise sensor information can imported in either of these formats.
Notes
Failing To Connect
Upcoming Changes
Further Information
git, sugarlabs, bugs, translations, contacts, forums
[2] [http://br-gogo.sourceforge.net/ Br-GoGo Project Website