Sugar System Stack: Difference between revisions
Appearance
No edit summary |
m update link |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Sugar]] is implemented on top of existing or modified operating systems and hardware. Sugar [[Activities]] ("Sugarized applications") are accessed by the user in the Sugar platform, integrated into a single Journal for storage, and are often designed with peer collaboration as a primary feature. | [[What is Sugar?|Sugar]] is implemented on top of existing or modified operating systems and hardware. Sugar [[Activities]] ("Sugarized applications") are accessed by the user in the Sugar platform, integrated into a single Journal for storage, and are often designed with peer collaboration as a primary feature. | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 24 January 2012
Sugar is implemented on top of existing or modified operating systems and hardware. Sugar Activities ("Sugarized applications") are accessed by the user in the Sugar platform, integrated into a single Journal for storage, and are often designed with peer collaboration as a primary feature.
| Journal Content |
meta-tagged content datastore | |||||||
| Sugar Activities |
Browse | Chat | Read | Write | Record | EToys | Turtle Art | Terminal | et al... | |||||||
| Sugar Platform |
Sugar Platform Stack: Sugar Framework and Sugar Software Stack | |||||||
| Operating System |
Fedora | Debian | Ubuntu | Linux, other | LTSP | Mac OSX | MS Windows (emulation) | ... | |||||||
| Hardware Platform |
OLPC XO-1 |
ASUS EEE PC |
Intel Classmate |
OLPC XO-2 |
... | |||
The layers in a Sugar system are:
- Journal
- Activities
- Sugar Platform Stack
- Operating System
- Computer Hardware
Sugar System Stack (ASCII Text)
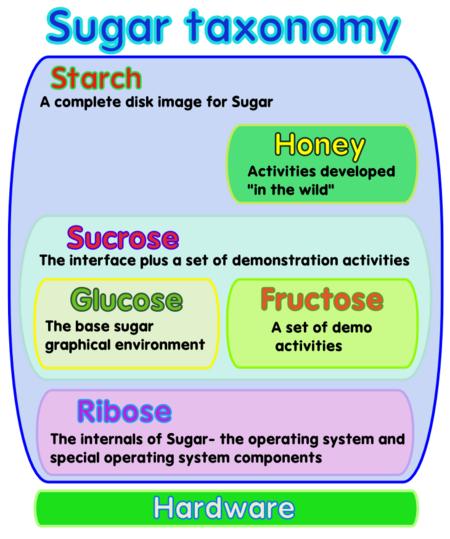
Sugar Labs has borrowed names from carbohydrate chemistry, which includes sugar, to personalize and help distinguish pieces of Sugar software. See Taxonomy and On the Naming of Sugar for background.
System Stack Illustration